API 서버 학습 : Locust 부하테스트
부하테스트
Locust를 써서 현재의 “기본 게시판”이 얼마나 부하를 견디는지 보고, 이후에 붙일 것들을 생각해봐야 한다.
우선 현재의 엔드포인트들을 한 번 확인해본다:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
import random
from locust import HttpUser, between, task
USERS = [
{"username": "user1", "password": "pass1"},
{"username": "user2", "password": "pass2"},
{"username": "user3", "password": "pass3"},
]
class BoardUser(HttpUser):
token: str = None
headers: dict = {}
post_ids: list[int] = []
wait_time = between(1, 3)
def on_start(self):
creds = random.choice(USERS)
response = self.client.post("/auth/login", data=creds)
if response.status_code == 200:
self.token = response.json().get("access_token")
self.headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.token}"}
else:
print("Login failed", response.text)
self.headers = {}
posts_response = self.client.get("/posts/", headers=self.headers)
if posts_response.status_code == 200:
posts = posts_response.json()
self.post_ids = [post["id"] for post in posts]
@task(5)
def list_posts(self):
self.client.get("/posts/", headers=self.headers)
@task(1)
def create_post(self):
if not self.token:
return
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.token}"}
post_data = {
"title": f"Post title {random.randint(1, 10000)}",
"content": "This is a sample post content for load testing.",
}
response = self.client.post("/posts/", json=post_data, headers=self.headers)
if response.status_code == 201:
post = response.json()
self.post_ids.append(post["id"])
@task(2)
def create_comment(self):
if not self.post_ids:
return
post_id = random.choice(self.post_ids)
comment_data = {
"post_id": post_id,
"content": f"Comment content {random.randint(1,10000)}",
}
self.client.post("/comments/", json=comment_data, headers=self.headers)
미리 만들어둔 3개의 테스트 계정을 이용하여 엔드포인트들을 테스팅하도록 했다.
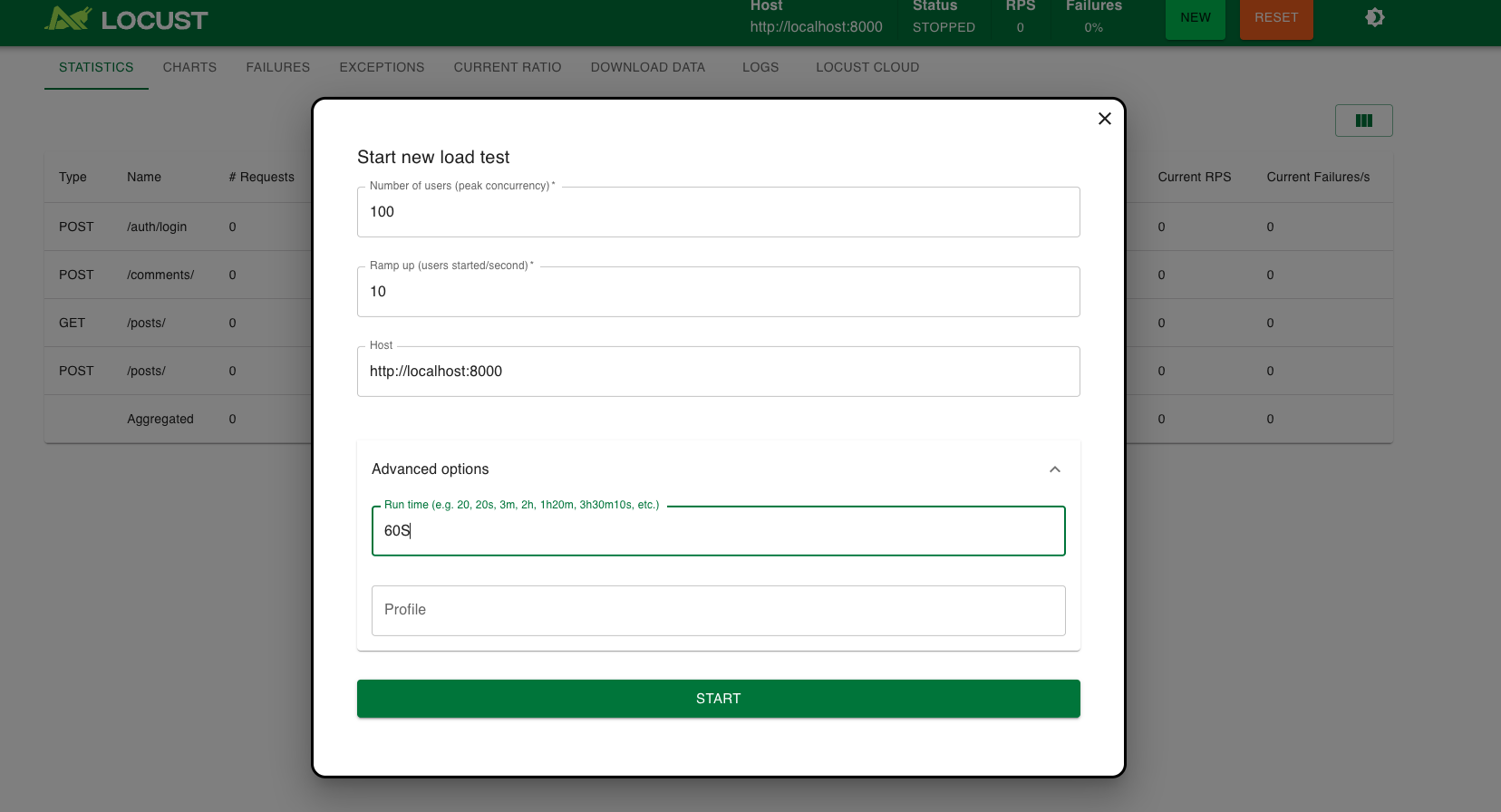
Sanity Check를 위해 100명의 사용자로 60초동안 테스팅하도록 설정했다.
요청들은 다 성공했고, 로그인을 제외하면 중위값 7ms로 빨랐다. 로그인은 hash때문에 salt에 영향을 받으며, 이는 필요에 따라 조정 가능한 수치이기도 하지만 로그인을 빈번하게 할 필요가 없다면 중위값 4.4초도 나쁜 속도가 아니지만 p95인 10초와 p99인 16초는 좀 문제가 있어 보인다. 이쪽은 조정이 필요해보여 변경하기로 했다:
bcrypt__rounds를 10으로 변경해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
pwd = CryptContext(
schemes=["bcrypt"],
deprecated="auto",
bcrypt__rounds=10,
)
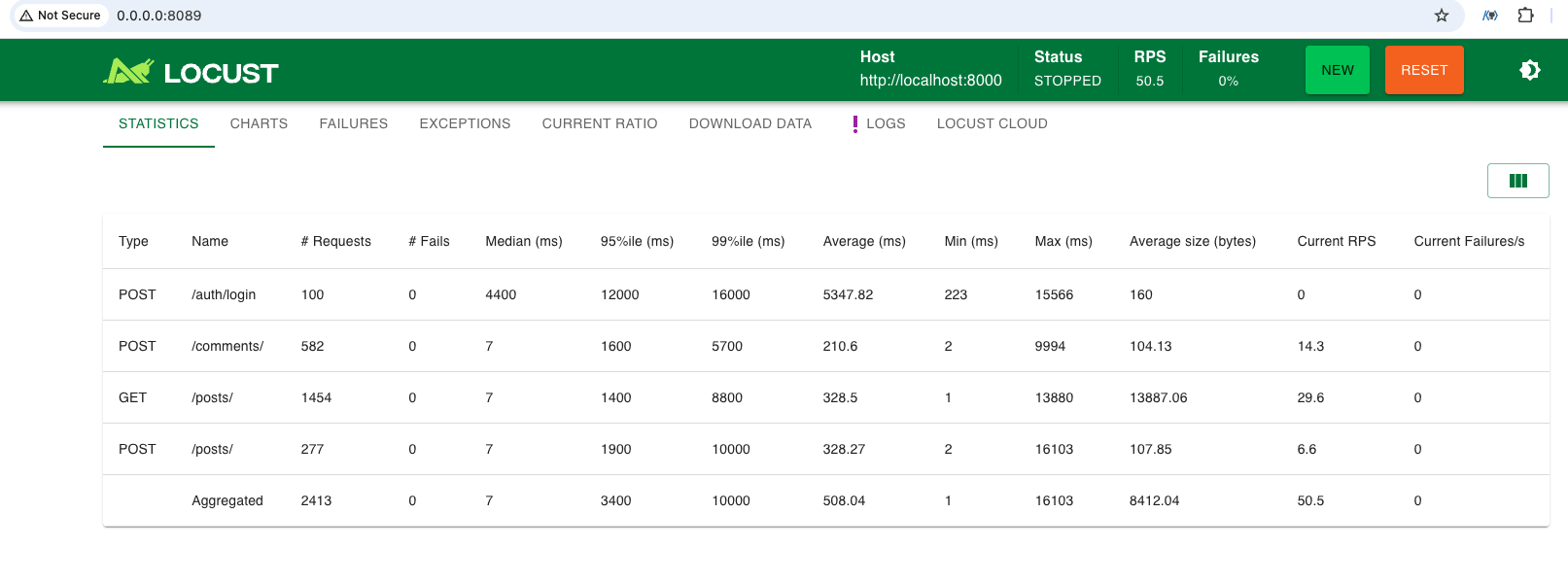
로그인쪽은 당연히 성능 개선이 되었는데, 로그인 이외에 부분에서도 유의미한 속도 증가가 일어났다.
원인은, 다음으로 추측된다:
- bcrypt연산에 사용되는 컴퓨팅 리소스가 감소
- 파이썬의 GIL을 hashing과정에서 잡고있었는데, 이게 다른 코루틴 실행 대기를 시키고 있었음
- DB쿼리의 실행/반환 지연
또한, verify/hash가 동기 함수이기 때문에 event loop를 블로킹하고 있었을 것이다.
FastAPI Async에서는 병목을 발생시킬 수 있는 포인트이기에, bcrypt와 로그인 verify도 백그라운드에서 실행시킬 필요가 있다.
hash관련 로직을 별도로 분리하고, 이를 UserService에서 import하여 사용하도록 했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
#hash.py
import asyncio
from passlib.context import CryptContext
pwd = CryptContext(
schemes=["bcrypt"],
deprecated="auto",
bcrypt__rounds=10,
)
async def hash_password(password: str):
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
return await loop.run_in_executor(None, pwd.hash, password)
async def verify_password(password, hashed):
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
return await loop.run_in_executor(None, pwd.verify, password, hashed)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#user_service.py
class UserService(UserServiceInterface):
def __init__(self, repo: UserRepositoryInterface):
self._repo = repo
async def create_user(self, data: UserCreate) -> User:
hashed = await hash_password(data.password)
user = User(username=data.username, password=hashed)
return await self._repo.create(user=user)
async def authenticate(self, username: str, password: str) -> User | None:
user = await self._repo.get_by_username(username=username)
if not user:
return None
if not await verify_password(password, user.password):
return None
return user
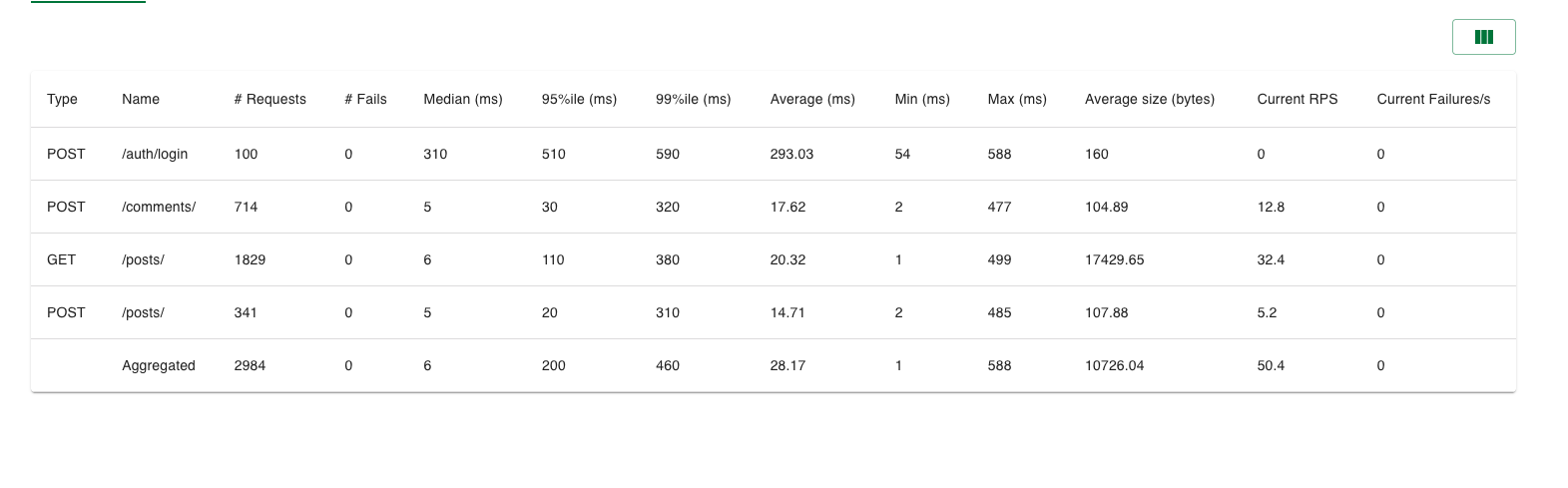
위 처리를 하고 나니 획기적으로 시간이 줄었다.
더 높은 부하
이제는 조금 더 높은 부하로 테스팅을 해보아야 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
File "/Users/jaeheenam/Dev/personal/fastapi_crud/.venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/sqlalchemy/pool/base.py", line 1264, in _checkout
fairy = _ConnectionRecord.checkout(pool)
File "/Users/jaeheenam/Dev/personal/fastapi_crud/.venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/sqlalchemy/pool/base.py", line 711, in checkout
rec = pool._do_get()
File "/Users/jaeheenam/Dev/personal/fastapi_crud/.venv/lib/python3.13/site-packages/sqlalchemy/pool/impl.py", line 166, in _do_get
raise exc.TimeoutError(
...<4 lines>...
)
sqlalchemy.exc.TimeoutError: QueuePool limit of size 5 overflow 10 reached, connection timed out, timeout 30.00 (Background on this error at: https://sqlalche.me/e/20/3o7r)
ERROR: Exception in ASGI application
바로 실패하기 시작했다.
우선 쿼리풀(=커넥션 풀)을 pool size를 20으로 늘려준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
engine = create_async_engine(
settings.DATABASE_URL,
echo=False,
future=True,
pool_size=20, #디폴트(5) -> 20으로 늘림
max_overflow=20, #디폴트(10) -> 20으로 늘림
)
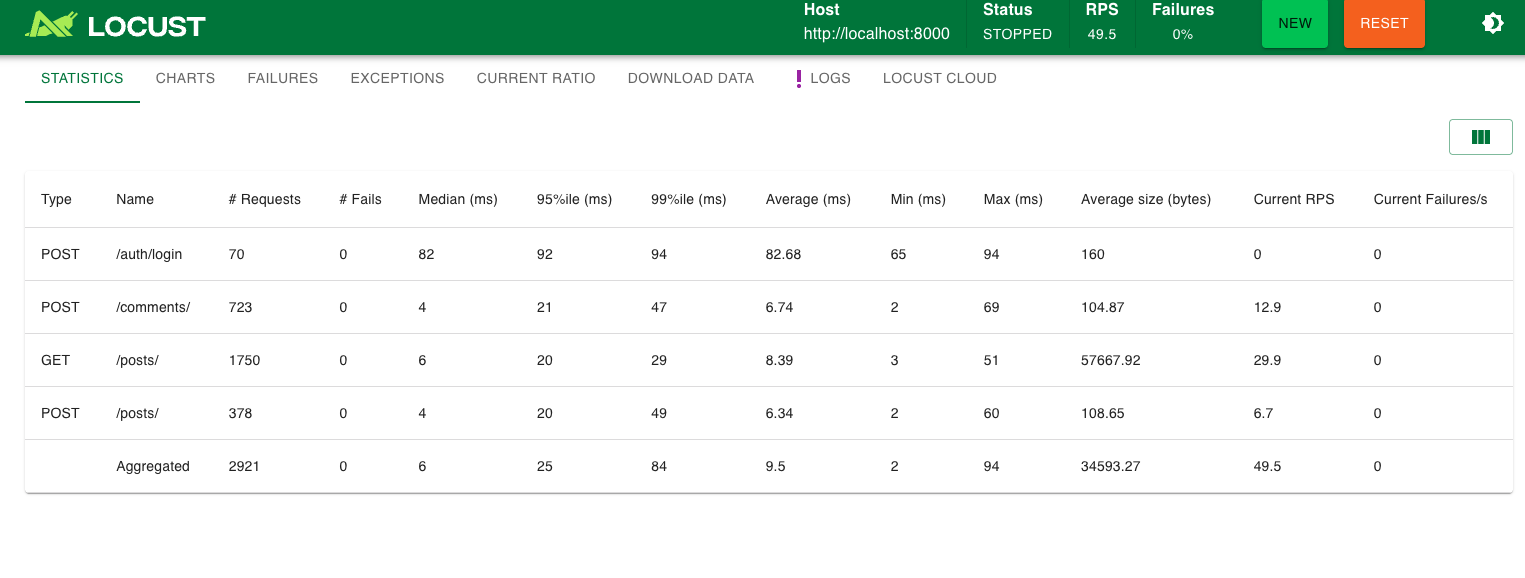
여전히 실패하는 것을 볼 수 있다. p95와 p99가 30/31초인 이유는 타임아웃이 30초이기 때문이다. 시간이 오래 걸려서 실패한다는 것을 확인할 수 있는 지표이다.
당장 빠르게 적용해볼 수 있는 개선법은 캐싱일 것이다. 로커스트를 살펴보면, GET posts가 가장 빈번하게 실패를 하고 있기 때문에 (11.1/s), 전체 목록을 캐싱하도록 다음 번에 적용해보겠다.