API 서버 학습 : 응답 캐싱
응답 캐싱
레디스를 사용해서 캐싱을 추가헀다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#redis.py
from redis.asyncio import Redis
class RedisConstants:
CACHE_KEY_POST_ALL = "posts:all"
CACHE_TTL_POSTS = 60
redis = Redis.from_url(
"redis://localhost:6379/0",
encoding="utf-8",
decode_responses=True,
)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#post_rounter.py
@router.get("/", response_model=list[PostOut])
async def list_posts(
post_service: PostService = Depends(get_post_service),
):
cached = await redis.get(RedisConstants.CACHE_KEY_POST_ALL)
if cached:
return json.loads(cached)
posts = await post_service.list_posts()
posts_out = [PostOut.from_orm(p) for p in posts]
await redis.set(
RedisConstants.CACHE_KEY_POST_ALL,
json.dumps([p.model_dump() for p in posts_out]),
ex=RedisConstants.CACHE_TTL_POSTS,
)
return posts
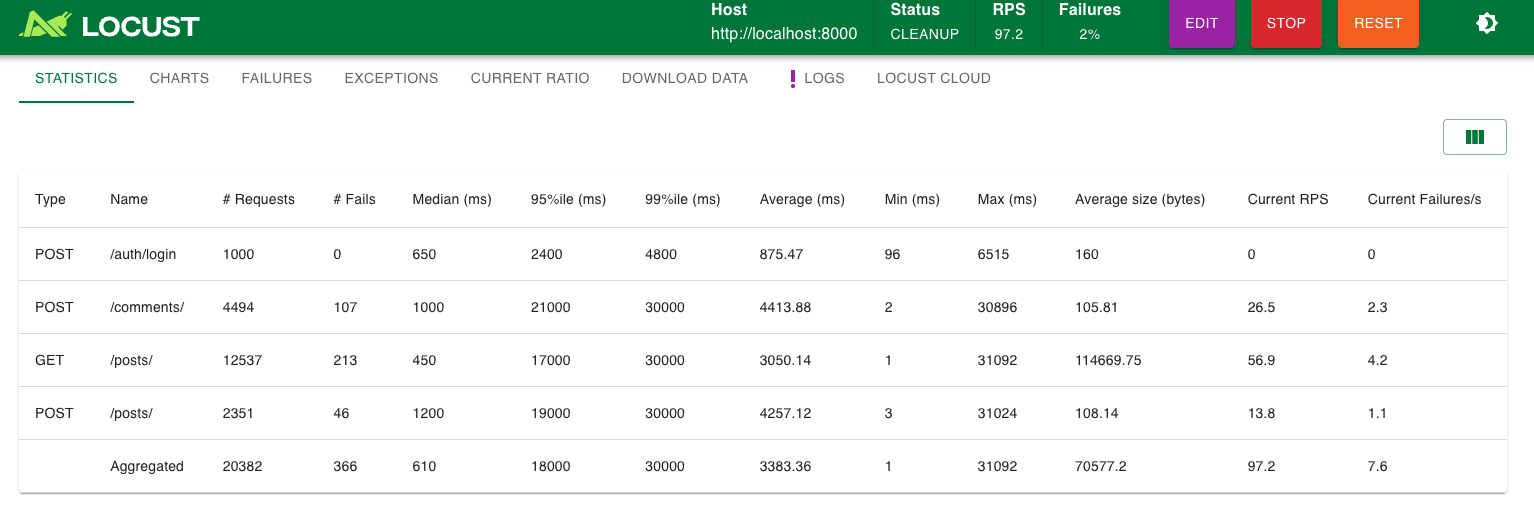
우선 실패 빈도가 확연히 줄었다. 기존에 실패하던 원인이 커넥션 풀 때문인 것을 생각해보면, 조회 빈도가 삽입빈도보다 5배 더 많은 현재 부하 테스팅 환경에서는 캐싱을 함으로 데이터베이스 I/O를 획기적으로 줄일 수 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
1
sqlalchemy.exc.TimeoutError: QueuePool limit of size 20 overflow 20 reached, connection timed out, timeout 30.00 (Background on this error at: https://sqlalche.me/e/20/3o7r)
여전히 위와 같은 커넥션 풀 타임아웃 오류가 발생하기 때문에 p99는 30초이다.
추가 안정성과 속도 개선을 위해 정확한 측정이 필요해보인다. 다음번엔 Prometheus & Grafana 스택을 사용하여 보다 정밀하게 파악해보자.
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.