디자인 패턴 - 옵저버, 이터레이터, 노출모듈 패턴
옵저버 패턴
주제가 어떤 객체의 상태 변화를 관찰하다가 상태 변화가 있을 때마다 메서드 등을 통해 옵저버 목록에 있는 옵저버들에게 변화를 알려주는 패턴이다. 여기서 말하는 주제란, 객체의 상태 변화를 보고 있는 관찰자이며, 옵저버는 이 객체의 상태 변화에 따라 전달되는 메서드 등을 기반으로 추가적인 변화 사항들이 생기는 객체들이다. 때로는 주제와 객체를 별도로 분리하지 않고 상태가 변경되는 객체를 기반으로 구축되기도 한다.
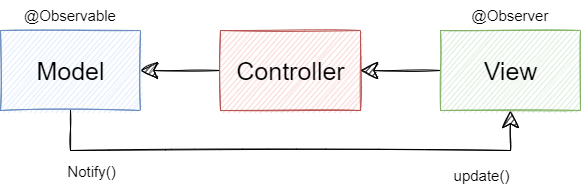
예를 들어서, X의 경우 내가 일론 머스크를 팔로우했다고 가정하면 일론 머스크가 포스팅을 할 시 알림이 나에게 와야 한다. 이렇게 주로 이벤트 기반과 알림 시스템에 사용되며, MVC패턴에도 사용된다. 객체인 Model에 변경 사항이 생기면 update()메서드로 옵저버인 View에 알려주고, 이를 기반으로 Controller가 작동하는 것이다.
날씨 변경과 이에 따라 옵저버들에게 해당 정보들을 쏴주는 코드로 옵저버 패턴 예시를 들어보자:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
// 주제 인터페이스
interface Subject {
void registerObserver(Observer o);
void removeObserver(Observer o);
void notifyObservers();
}
// 옵저버 인터페이스
interface Observer {
void update(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure);
}
// 구체적인 주제: WeatherData
class WeatherData implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers;
private float temperature;
private float humidity;
private float pressure;
public WeatherData() {
observers = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void registerObserver(Observer o) {
observers.add(o);
}
public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
observers.remove(o);
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (Observer observer : observers) {
observer.update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
}
}
public void setMeasurements(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.humidity = humidity;
this.pressure = pressure;
notifyObservers();
}
}
// 구체적인 옵저버: CurrentConditionsDisplay
class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer {
private float temperature;
private float humidity;
public void update(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.humidity = humidity;
display();
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Current conditions: " + temperature + "C degrees and " + humidity + "% humidity");
}
}
// 테스트 클래스
public class WeatherStation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
CurrentConditionsDisplay currentDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay();
weatherData.registerObserver(currentDisplay);
weatherData.setMeasurements(30.5f, 65.0f, 1013.1f);
weatherData.setMeasurements(28.2f, 70.0f, 1012.5f);
}
}
위 코드로 옵저버 패턴을 설명해보자면, 옵저버 클래스 CurrentConditionsDisplay는 객체 WeatherData의 registerObserver, removeObserver, notifyObservers 메서드들을 통해 관리된다. 객체 WeatherData의 변수인 temperature, humidity, pressure이 변경될 때마다 registerObserver를 통해 옵저버 목록에 등록된 옵저버들에 notifyObserver 메서드를 통해 상태 변화에 대해 알려 옵저버들의 temperature과 humidity값도 업데이트한 후 해당 값들을 출력하도록 한다.
이터레이터 패턴
이터레이터 패턴은 인터레이터(Iterator)를 사용하여 컬렉션의 요소들에 접근하는 디자인 패턴이다. 순회할 수 있는 여러 가지 자료형의 구조와는 상관없이 이터레이터라는 하나의 인터페이스로 순회가 가능해진다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
const mp = new Map()
mp.set('a', 1)
mp.set('b', 2)
mp.set('c', 3)
const st = new Set()
st.add(1)
st.add(2)
st.add(3)
for (let a of mp) console.log(a)
for (let a of st) console.log(a)
mp는 맵 자료구조의 인스턴스이며, st는 세트 자료구조의 인스턴스로 서로 다른 자료구조임에도 for a of b문법을 통해 순회가 가능하다. 즉, for a of b문법은 인터레이터 프로토콜이다.
이렇게 이터레이터 프로토콜은 언어에 내장된 경우가 많으며, 일관된 접근 방식을 제공하여 여러 자료형을 다루기 쉽게 한다. 자바로 예시를 들면 다음과 같다:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class User {
private String name;
private String email;
public User(String name, String email){
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
}
public class IteratorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
User u1 = new User('jae', 'j@example.com');
User u2 = new User('kay', 'k@example.com');
users.add(u1);
users.add(u2);
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
for (User user: users){
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
for (int num: set){
System.out.println(num)
}
}
}
위와 같이 for-each 문이라는 단일 순회 방식을 사용하여 서로 다른 두 자료형의 컬렉션을 순회할 수 있다.
노출모듈 패턴
노출모듈 패턴은 즉시 실행 함수를 통해 private, public, protected 등과 같은 접근 제어자를 만드는 패턴이다. 자바에서는 선언으로 가능하지만, 자바스크립트에서는 이런 접근 제어자가 존재하지 않고 전역 범위에서 스크립트가 실행되기 때문에 노출모듈 패턴을 통해 public이나 private과 같은 접근 제어자를 구현한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
const pattern = (()=> {
const a = 1;
const b = 2;
const public = {
c : 2,
d : () => 3,
sum : () => a + b
}
return public
})()
console.log(pattern)
console.log(pattern.a)
console.log(pattern.sum)
// { c : 2, d : [Function : d]}
// undefined
// 3
a와 b는 다른 모듈에서는 사용할 수 없는 변수로 private 범위를 가진다. c와 d는 다른 모듈에서 사용할 수 있는 변수나 함수이며 public 범위를 갖는다. 여기서 a와 b가 private 범위를 가지는 이유는 함수의 스코프 때문인데, 즉시 실행 함수 내부에서 정의된 변수는 함수의 스코프 내에서만 유효하기 때문에 외부에서 접근이 불가능하다. 반면, public이라는 객체는 반환 값으로 외부에 노출이 되기에 외부에서 접근 가능하다.
그렇다면, a와 b에 접근할려면 어떻게 해야할까?
자바에서 익히 다룬 getter 과 setter을 사용하는 방법이 떠오른다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
const pattern = (()=> {
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
const publicObj = {
c : 2,
d : () => 3,
sum : () => a + b,
setA : (newA) => a = newA,
getA : () => a,
setB : (newB) => b = newB,
getB : () => b
}
return publicObj;
})()
이렇게 pattern 함수를 구현하게 되면 pattern.setA(3) 를 하면 내부 a값이 변경되고, pattern.getA()를 사용하여 값을 가져올 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
const pattern = (()=> {
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
const publicObj = {
c : 2,
d : () => 3,
sum : () => a + b,
setA : (newA) => a = newA,
getA : () => a,
setB : (newB) => b = newB,
getB : () => b
}
return publicObj;
})()
console.log(pattern.getA()); // 1
pattern.setA(3);
console.log(pattern.getA()); // 3
정리
옵저버 패턴
- 특정 객체의 상태 변화에 따른 알림을 주어 해당 객체의 정보를 기반으로 작동하는 옵저버들이 반응하도록 함
- 객체의 상태 변화가 일어날 시 notify()등의 메서드를 사용하여 옵저버들의 update()메서드를 실행하여 옵저버는 새로운 상태 정보를 받아 업데이트
이터레이터 패턴
- 다양한 이터러블 자료구조에 대해 일관된 방식으로 순회 가능 : 개발자는 각 자료구조의 내부 구현에 대한 지식 없이도 쉽게 데이터 순회 가능
- 컬렉션의 내부 구조를 숨기고 데이터 접근을 위한 표준 인터페이스 제공, 팩토리 메서드 패턴과 비슷하게 컬렉션의 구현 세부사항을 변경해도 이터레이터 인터페이스를 사용하는 클라이언트 코드를 변경할 필요 없음
노출모듈 패턴
- 접근 제어자가 제공되지 않는 언어에서 객체에 대한 접근 제공자 설정 가능
- 자바스크립트 기준 즉시 실행 함수를 사용하여 내부 변수(Private)를 정의하고, 외부에서 접근할 수 있는 메서드(Public)을 반환하여 객체에 대한 접근 권한 설정 가능